Quick Summary:
Are you still following on-premise IT solutions, handling all the expenses, and managing all the tasks all by yourself? Do you want to shift from on-premise to cloud computing solutions but cannot distinguish the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS? This blog will compare IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS in detail to assist you in making the right decision for meeting your business requirements.
Cloud computing is gradually gaining importance and wider acceptance from small businesses, mid-scale organizations, and enterprises for significantly improving overall productivity and efficiency without burning holes in their pockets or losing crucial business data. With so many different cloud computing options available, most non-technical businesses often get overwhelmed and confused about which software solutions to leverage and how to implement them in their business operations efficiently.
Quick Overview of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services
Let us understand the fundamental differences between Cloud IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services without wasting time.
Difference between SaaS PaaS and IaaS in Tabular Form
| Points | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Examples | – Rackspace – Microsoft Azure – Google Computing Engine (GCE) |
– AWS Elastic Beanstalk – Heroku – Google App Engine – OpenShift – Windows Azure |
– Dropbox – Salesforce – Cisco WebEx – GoToMeeting – Google Workspace |
| Description | Virtual Infrastructure | Focus on Application Logic | Software Licensing |
| Base Layer Unit | Virtual Machine | Application | Software |
| Good For | Existing Systems | Web App Development | Low-risk daily tasks |
1. What is IaaS in cloud computing?
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service. It provides support for web apps, storage, application, web servers, and networking resources. By implementing IaaS, cloud computing solutions in your business processes, you can easily scale your infrastructure up or down to adjust to the unpredictable demand for your app.

Key Features of IaaS
- Multi-Tenancy & Billing Management.
- Monitoring & Logging.
- Clustering, Failover & Load Balancing.
- Backup, Replication, and Data Recovery.
When to use IaaS?
When you…
- want complete control of your enterprise-grade application.
- are in a growing phase and expect your application to grow over time.
- want to increase reliability, security, and supportability.
- want to focus on your core business.
- have dedicated IT team to handle Infrastructure Services.
IaaS Strengths and Limitations
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Flexible cloud computing model. | Giving up security to a certain extent. |
| Automate storage, networking, servers, and processing power with ease. | Lack of flexibility. |
| Pay for resources as and when needed. | Over Dependency. |
| Complete control of infrastructure. | Upgrade and Maintenance. |
| Highly scalable. | Technical difficulties. |
2. What is PaaS Cloud Computing?
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. It leverages virtualization for offering an application development platform to organizations and individual developers. PaaS platform covers an all-inclusive list of services like memory, storage, database, and other reliable app development solutions.
Key Features of PaaS
- Multi-tenant architecture.
- Robust workflow engine/capabilities.
- Flexible ‘service-enabled integration model.
- Control over security/sharing through permission model.
- Customizable user interface.
When to use PaaS?
When you…
- need high computing power to run complex operations.
- need secure, unlimited, and flexible data storage options.
- Want to shift an application ‘as-is’ from on-premise to cloud computing.
PaaS Strengths and Limitations
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Helps streamline production. | Can be incompatible with many systems. |
| Fast and flexible tools. | Poor access to support. |
| Access from anywhere. | Third-party may not work well with the current business model. |
| Cost-saving on in-house IT dependencies. | Can’t manage security in-house. |
| Transitioning from one platform to another can be challenging. |
3. What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. It allows users to connect to the cloud and leverage cloud-based apps over the internet. SaaS applications are often used by almost all businesses and in our day-to-day lives as well. It provides applications on the web as a service.
Key Features of SaaS
- Multi-tenancy model.
- Automated provisioning.
- Single sign-on.
- High availability.
- Data security.
- Application security.
When to use SaaS?
When you…
- need to work with emails.
- need to set up desktop as a service/Virtual desktop.
- want to improve your testing and development.
- want to utilize big data analytics.
- build custom software like CRM, HRM, and ERP.
SaaS Strengths and Limitations
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Simpler and affordable costing system. | Security concerns as third-party vendors don’t take any responsibility for your applications. |
| Hassle-free and automatic maintenance. | SaaS offering compliances can be difficult to understand. |
| Great mobility and flexibility. | Businesses lose all control over their applications. |
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS Detailed Comparison with Use Cases
Now that we are clear with the basic functionality and capabilities of cloud computing services SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, we should try to understand the differences between all three of them in comparison to one another.
1. SaaS vs IaaS
What is the difference between IaaS And SaaS?
Going for a SaaS product will give you the most services from your third-party provider regarding software management and maintenance costs and services. In contrast, IaaS only provides and maintains core components such as storage or servers, and the rest of the processes need to be managed by the users.
Whether you should go for Software as a Service or Infrastructure as a Service will highly depend on the targets that you are trying to achieve. Suppose you are working on a comparatively large-scale project where you cannot afford to hand over management to external service providers and risk compromising the functionality or security of your data. In that case, you should opt for IaaS and retain control. Whereas, if you are working on a project where you do not need a lot of flexibility and prioritize ease of use over security concerns, opting for an effective SaaS solution is a better option.
2. IaaS vs PaaS
What is the difference between IaaS and PaaS?
As we saw in the previous comparison, IaaS provides great control to the users over their operating systems based on your cloud-computing environment. In comparison, PaaS solutions can help developers build apps without hosting them on-site, providing more options and flexibility in exchange for a little loss of control.
For instance, if you are planning to build a simple and straightforward website, you can utilize IaaS products like Amazon Web Services to assist you with the needed infrastructure to set up your site’s hosting and its applications. However, for adding custom features to your website or web app development solution, you will need a PaaS product like Google App Engine that allows you to host your website and develop and design custom apps.
3. PaaS vs SaaS
What is the difference between PaaS and SaaS?
Platform as a Service can be used for creating new products on a pre-existing network. On the other hand, SaaS products provide entire freedom to the users by completely managing all the requirements to make a ready-to-use solution for your teams.
Suppose you have a project to create a basic payroll app for your custom HR requirements. In that case, you have two possible options. You can either go for a PaaS solution to get all the necessary tools to create your custom payroll app to match your requirements or get an out-of-the-box easy-to-use payroll app by using existing payroll SaaS solutions like Quickbooks.
IaaS PaaS SaaS Market Share (Figures in Billions of USD)
| Cloud Computing Technologies | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Cloud Application Infrastructure Services (PaaS) | 11.9 | 15.4 | 18.8 | 23.0 | 27.7 |
| Cloud Business Process Services (BPaaS) | 42.2 | 46.6 | 50.3 | 54.1 | 58.1 |
| Cloud Application Servers (SaaS) | 58.8 | 72.2 | 85.1 | 98.9 | 113.1 |
| Cloud Management and Security Services | 8.7 | 10.7 | 12.5 | 14.4 | 16.3 |
| Cloud System Infrastructure Services (IaaS) | 23.6 | 31.0 | 39.5 | 49.9 | 63.0 |
| Overall Market | 145.3 | 175.8 | 206.2 | 240.3 | 278.3 |
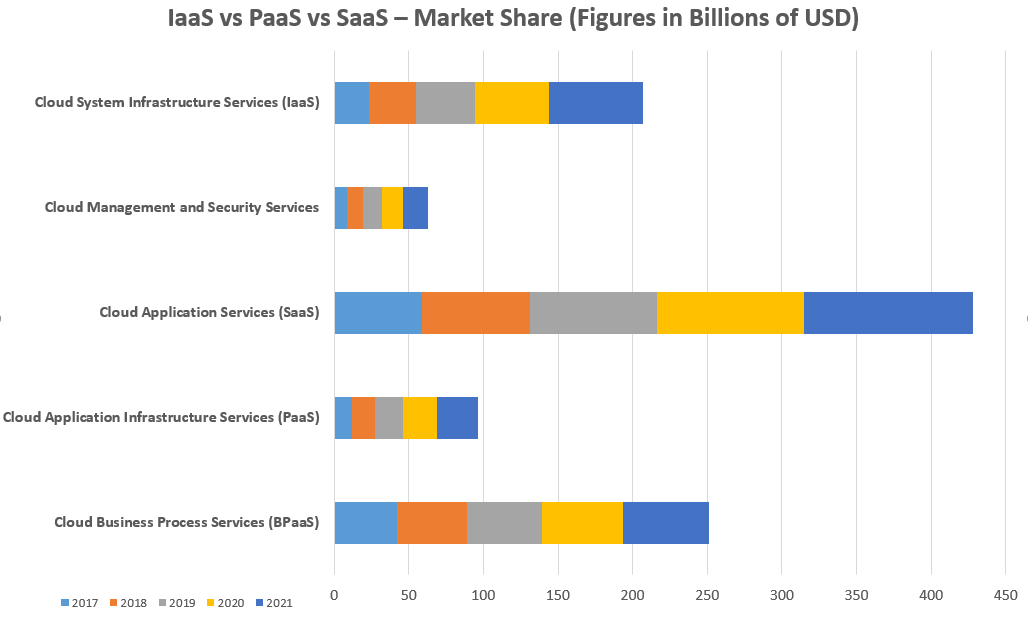
Gartner conducted a study on September 12, 2018, comparing the market growth forecast of various cloud-computing services. The fastest-growing segment of the overall market belonged to cloud system infrastructure services (IaaS), which was forecasted to grow by 27.6 percentage in 2019, reaching $39.5 billion from its value of $31 billion back in 2018. Compared to PaaS, SaaS, and IaaS, SaaS adaptation forecast saw the largest growth, then IaaS and then PaaS. This study also forecasted that 90 percent of businesses purchasing public cloud IaaS services would do so from an integrated IaaS and PaaS provider for leveraging the benefits of both these services.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS – Control vs Ease of Management
One thing you need to understand is IaaS, PaaS and SaaS are not mutually exclusive services. Most organizations use them in pairs or use different combinations of the three to carry out their business activities, and some even combine them with traditional IT practices.
Generally, the ‘as-a-service solution a company chooses depends on the requirements and expertise to leverage the most out of those services. For instance, if an organization does not have in-house IT expertise, it will not benefit much from leveraging IaaS solutions.
However, for some cases, the deciding factor between the three as-a-service models comes down to which model provides the most cost-efficient, viable, and accurate solution to the problem. In such cases, management generally decides on an as a service based on the control they can afford to give up versus the management ease they offer.
Building an ERP Solution with IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
| Platform | ERP Approach | Control | Management Burden |
| IaaS | You can build the backend IT infrastructure on the cloud using cloud IaaS solutions to build your development platform and application.
|
You get complete control over your operating systems and configurations. | You take all management burden of managing and maintaining these services, developing the platform and application. |
| PaaS | You can alternatively build a custom CRM application and outsource application and infrastructure management to your PaaS provider. | You get complete control over your application features. | You would be responsible for managing your application and the associated data. |
| SaaS | Another alternate is to choose a SaaS-based CRM solution and outsource all management tasks to a third-party vendor. | You get no control over the features and functionality, data storage, or security. | You do not have to manage anything. |
On-Premise vs Cloud Key Differences
Understanding the limitations and capabilities of the on-premise (traditional) approach is important to understand why cloud-computing services became necessary and beneficial to organizations globally.
On-Premise Software
On-Premise Software requires the organization to purchase a copy of the software for using it. Since the software is licensed and within the organization’s premises, it provides better protection and peace of mind than a cloud-computing infrastructure.
Why do businesses still prefer cloud-computing solutions to on-premise solutions?
The costs associated with managing and maintaining all on-premise solution expenses can be significantly higher than those of a cloud-computing environment. It puts a heavy burden on the business. The organization needs to arrange for in-house server hardware, software licenses, integration capabilities, and a skilled technical workforce to support and manage any glitches or challenges. To stop this, they also need to worry about the regular maintenance costs to keep the software working efficiently.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is different from on-premise software. Instead of hosting everything in-house, a third-party provider hosts all the services on your behalf. One of the biggest advantages of this is that companies can pay-as-need and efficiently scale up or down depending on the company’s overall needs targets and growth. Besides, depending on your service, you can get instant, ready-made solutions that come pre-configured, such as SaaS tools.
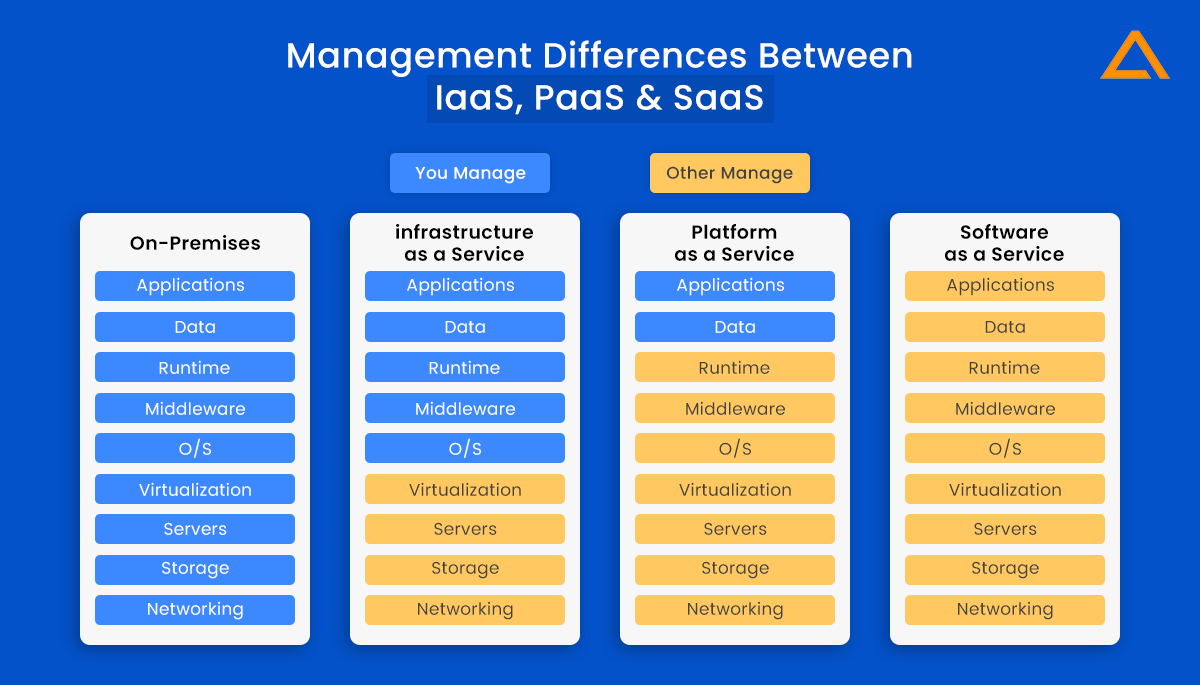
Management Differences between On-Premise vs IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
What’s New? Other Cloud Computing Delivery Models Explained
In the scheme of XaaS (Everything as a Service), SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are the most frequently known and used cloud computing delivery models. However, many other services can be beneficial for different business requirements as well. Here are some of them for your reference –
| Cloud Computing Delivery Models | Description |
| CaaS – Container as a Service | Helps manage and deploy apps using container-based abstraction. Can be deployed on-premise and cloud solutions, both. |
| FaaS – Function as a Service/Serverless Computing | Provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage app functionalities without building and maintaining infrastructure. |
| DaaS – Desktop as a Service | Delivers virtual desktops to end-users over the internet that are licensed with a pay-per subscription. They can also be used for handling security and applications for desktops. |
| MBaaS – Mobile Backend as a Service | Uses a service provider to handle and power the backend services like business logic and data management of an app. |
Wrapping up!
This is the ultimate cloud PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS comparison for you to better understand which cloud computing service to use for your business requirements. Remember, they are not standalone solutions and can be used in any permutation and combination. Going for a hybrid comprehensive cloud solution could help you take care of many business aspects, reducing your overheads and freeing up more time on your hand to focus on your core business goals and objectives.