Quick Summary:
As manufacturing steps into a smarter, more connected future, Generative AI is quickly becoming a game-changer. From simulating production lines and generating personalized training to streamlining supply chains and enhancing maintenance systems, GenAI blends creativity with real-time data. In this blog, we explore how GenAI is being used in real-world factories, its benefits, and how manufacturers can start using it to build more agile, efficient, and intelligent operations.
In this blog, we’re going to discuss📝
- What is Generative AI and How Is It Different From Traditional AI?
- Why Generative AI Is the Perfect Fit for Modern Manufacturing?
- Why Manufacturers are Turning to GenAI Now?
- Top Use Cases of Generative AI in Manufacturing
- Building Smarter Factory Systems with Generative AI
- Challenges and Risks of Adopting GenAI in Manufacturing
- Roadmap to Implementing GenAI in Manufacturing
- The Future of Generative AI in Manufacturing
Manufacturers are no longer just automating workflows but they’re also teaching machines to think, design, and adapt. At the core of this shift is Generative AI, bringing intelligence to every layer of the factory floor. While traditional AI has played a role in optimizing specific tasks and streamlining repetitive processes, we’ve now entered an era where machines don’t just execute but they create, adapt, and assist in decision-making with unprecedented sophistication.
What Is Generative AI and How Is It Different from Traditional AI?
Manufacturers have used AI before but mostly for spotting patterns, flagging issues, or forecasting trends. Generative AI (GenAI) takes it a step further. It doesn’t just analyze existing data it creates something new from it.
In the manufacturing world, that means GenAI can assist in designing product concepts, simulating factory processes, or drafting work instructions all by learning from existing data and goals set by your team.
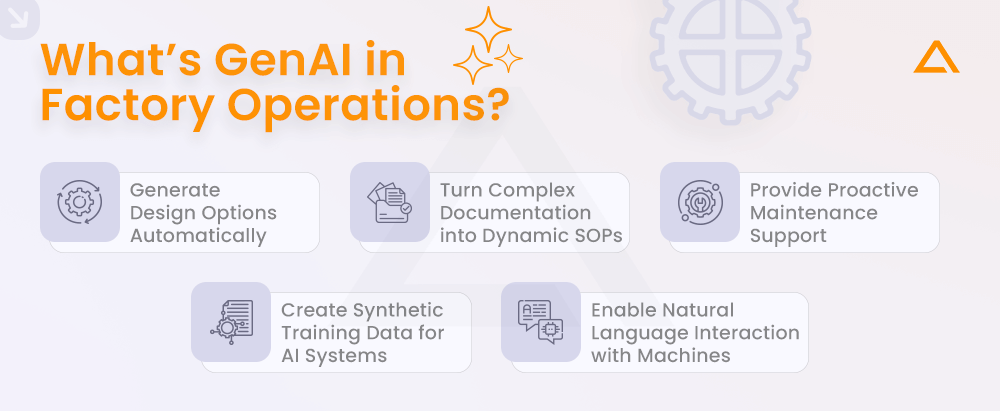
What Can GenAI Actually Help With on the Factory Floor?
GenAI supports manufacturing teams by making complex tasks faster and easier to manage. Here’s how:
- Generate part and product design ideas: Based on specs like materials, dimensions, or energy goals, GenAI can suggest multiple design options reducing time spent in early development.
- Turn old manuals into clear work steps: GenAI can read through long SOPs, compliance documents, and logs, then turn them into clean, step-by-step instructions for operators or technicians.
- Help plan maintenance smarter: GenAI can’t detect faults on its own (that’s still sensor-driven), but it can help by simulating wear scenarios, summarizing past maintenance, and creating service guides to support preventive planning.
- Train AI inspection tools with synthetic data: If your factory doesn’t have enough defect images, GenAI can generate realistic samples to help quality control systems learn what to spot.
- Enable chat-based support for workers: With the right setup, GenAI can power systems that answer shop floor questions in plain language like “How do I fix a motor fault on Line 4?”
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
Traditional AI has already brought huge value to factories, especially in process monitoring, predictive analytics, and anomaly detection. But generative AI Services is not an upgrade but a shift in capability.
| Traditional AI | Generative AI |
| Analyzes existing data | Generates new content and configurations |
| Predicts failures and issues | Simulates scenarios and suggests proactive changes |
| Requires large labeled datasets | Can create synthetic data to train itself or other models |
| Optimizes predefined processes | Designs entirely new workflows or part geometries |
What Powers GenAI Behind the Scenes?
Generative AI in manufacturing may look simple on the surface ask a question, get an answer, run a simulation but there’s powerful tech working in the background to make it happen.
Here’s a quick, easy-to-understand look at what fuels GenAI’s abilities:
Large Language Models (LLMs)
These are advanced systems trained on all kinds of data such as machine manuals, SOPs, or maintenance logs.
- They help GenAI understand manufacturing language and respond to questions in plain English.
- Example: A technician might ask, “How do I fix a belt jam on Line 3?” and get a helpful, accurate response.
Synthetic Data
When real-world data (like images of defective parts) is hard to collect, GenAI can generate synthetic but realistic examples.
- This is useful for training inspection systems or simulating rare issues especially when waiting for real defects would take too long or be too risky.
Simulation Models
GenAI can use past data and sensor input to run “what-if” scenarios virtually.
- Want to test a new assembly sequence or predict the impact of a machine slowdown?
- GenAI-powered simulations let you do that without disrupting the production line.
Why Generative AI Is the Perfect Fit for Modern Manufacturing?
Manufacturing has always evolved with innovation from steam engines to robotics. But today, the industry faces bigger, more complex challenges: unpredictable supply chains, skilled labor shortages, stricter sustainability demands, and rising customer expectations.
These aren’t some small problems they affect the whole operation.
That’s where generative AI in manufacturing steps in. It helps engineers quickly test and improve product ideas without long delays. It supports maintenance teams by summarizing equipment data and flagging potential issues early. And it makes life easier for technicians by offering real-time, step-by-step guidance often through chat-style AI assistants that understand natural language.
Why Manufacturers are Turning to GenAI Now?
For decades, manufacturers have focused on smarter machines and connected systems. Yet today’s challenges demand more than efficiency now they require adaptability and real-time intelligence. This is where generative AI in manufacturing stands out, adding a strategic layer that complements, rather than replaces, existing systems.
The Market Momentum Behind GenAI
Generative AI isn’t just a buzzword. It’s gaining real traction across industries and manufacturing is quickly catching up.
- According to recent research, the generative AI market in manufacturing is projected to reach $6.4 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of over 41%.
- Nearly 48% of manufacturing leaders surveyed by Capgemini believe GenAI will fundamentally reshape their operations.
- Pilot projects are already gaining momentum, especially in product design, predictive maintenance, and training automation.
Making Intelligence Accessible on the Shop Floor
One of the biggest changes generative AI in manufacturing brings is how it supports workers right on the factory floor not just in the office or IT department.
Instead of reading through dashboards or long reports, operators can now interact with GenAI using everyday language.
- From dashboards to dialogue: Workers can ask simple questions like “Why is Line 2 running slow?” and get quick, AI-generated suggestions which can be achieve through manufacturing-specific AI chatbot. This works when GenAI tools are trained on real-time factory data.
- Training on the go: New staff can get step-by-step instructions directly on-screen, powered by GenAI. This helps speed up onboarding and reduces the need for long classroom training.
- Hands-on task support: Whether it’s fixing a machine issue or adjusting settings, GenAI can assist with simple guidance based on current conditions especially when combined with existing shop-floor systems.
Top Use Cases of Generative AI in Manufacturing
Generative AI in manufacturing is no longer just hype as it’s being actively deployed on factory floors, in product design labs, and across digital supply chains. Among its many applications, a few have proven especially impactful, delivering real-world results like faster design cycles, predictive insights, and smarter operations.
And where does this transformation often begin? With design:
Product Design & Development
Designing a new product usually takes weeks of sketching, testing, and revisions. But generative AI in manufacturing is helping engineers cut that timeline dramatically by suggesting smart design options instantly.
What It Can Do:
- Generate 3D designs automatically: Engineers can enter goals like weight, material, or size. GenAI then suggests multiple design versions that meet those specs.
- Speed up prototyping: Instead of starting from scratch, teams can choose from pre-generated models and test them in digital tools like CAD or simulation software.
- Explore more ideas, faster: Want to try a lightweight version? Or test a unique shape? GenAI makes it easy to test options without building anything physical.
⚠️ Note: While GenAI can create design options and virtual models, engineers still need simulation tools (like CAD or digital twins) to test those designs for safety and performance.
Design Optimization Using Text-to-Image Tools
Designing a new product isn’t only about how it works buts it’s about how does it looks and fits in the real world. With generative AI, engineers can now type in basic ideas and instantly generate visual design suggestions, giving them something concrete to build on.
Here’s how it works:
- Just by typing a prompt like “rugged, lightweight casing for outdoor sensor”, GenAI can instantly generate rough design visuals.
- These visuals give designers a creative starting point to refine shapes, materials, or styles before jumping into CAD.
⚠️ Important: These AI-generated images aren’t final designs. Engineers still need traditional tools like CAD and simulation software to validate them.
Example: Toyota’s Text-to-Image Design Innovation
The Toyota Research Institute is already fusing AI-generated imagery with core engineering constraints. By integrating text-to-image models into their design process, they allow creative teams to visualize concepts that also respect critical parameters such as aerodynamic drag, cabin dimensions, and safety standards.
Instead of working in silos, design and engineering now speak the same language, with GenAI acting as the translator.
Predictive Maintenance
Once a product design is in motion, keeping machines up and running becomes the next priority. This is where generative AI in manufacturing proves its long-term value by helping factories stay one step ahead of breakdowns.
Unlike traditional maintenance plans based on set schedules, GenAI can help spot problems early using data your machines already produce.
How It Works:
- Finds unusual patterns early: GenAI can study real-time machine data like vibrations, heat, or pressure and spot small changes that may lead to bigger problems later.
- Alerts before things go wrong: Instead of waiting for equipment to fail, the system helps predict issues in advance, giving your team time to plan service and avoid costly downtime.
⚠️Note: Generative AI doesn’t replace predictive maintenance systems on its own but it complements them. It works best when integrated with existing IoT sensors, machine logs, and historical maintenance data already in your setup.
Simulation of Maintenance Schedules with Synthetic Data
In many factories, there’s just not enough past data on rare equipment failures. That’s where generative AI in manufacturing steps in with the ability to create synthetic data to simulate “what if” scenarios.
This means maintenance teams can:
- Test how different settings (like speed or temperature) affect wear and tear
- Try out maintenance strategies without stopping production
- Plan ahead for rare failures that haven’t happened yet
⚠️ Note: GenAI doesn’t invent real-world failures it just creates safe, data-backed estimates. These simulations still rely on input from historical trends and machine experts.
Example: Siemens Senseye Predictive Maintenance
A great real-world example of this is Siemens’ Senseye Predictive Maintenance platform. In early 2024, Siemens enhanced the platform with generative AI features bringing natural language querying and cross-equipment learning into the maintenance workflow.
Now, technicians don’t just get alerts. They can ask the system questions like:
“What’s the risk level of Pump #3 failing in the next 72 hours?”
Or
“What would be the ideal service interval if the operating load increases by 10%?”
By merging machine insights with GenAI’s conversational interface, Siemens is making predictive maintenance accessible and actionable even for non-experts.
Workforce Training & On-the-Job Assistance
While generative AI is transforming machines and inspections, its quiet revolution is happening where it matters most on the factory floor. Traditional training can’t keep pace with the complexity of smart manufacturing. GenAI in workforce development delivers real-time, personalized support that empowers teams, enabling productivity through intelligence and not just by automation.
Personalized Learning Paths, Task-Specific Instructions
Training isn’t one-size-fits-all and generative AI in manufacturing makes it easier to deliver exactly what each worker needs.
Here’s how it helps:
- Customized learning paths: GenAI can build training plans based on a person’s role, experience level, and daily tasks.
- Clear, visual instructions: It turns complex procedures into simple step-by-step guides with images or videos.
- Localized accuracy: GenAI can adjust instructions depending on the specific machines used at different factory sites.
⚠️ Note: These features often rely on integration with existing HR systems, machine data, and documentation libraries. GenAI doesn’t create training content entirely on its own and it tailors what’s already available.
GenAI-Driven Support Systems and Chat-Based Assistants
Beyond static training, generative AI can offer on-demand guidance right at the moment it’s needed.
- Workers can ask natural language questions like “How do I reset this PLC?” or “What’s the torque spec for this part?”
- GenAI searches across manuals, SOPs, training docs, and past tickets to find the right answer in seconds.
- These systems don’t just reduce downtime but they also boost worker confidence, reduce errors, and help new employees ramp up faster.
⚠️ Note: GenAI works best when trained on your company’s specific documents and systems. Out-of-the-box models need integration with internal knowledge bases to deliver accurate results.
Example: Lozier’s GenAI-Powered Smart Search
Retail store fixture manufacturer Lozier implemented a GenAI-enabled intranet platform with smart search functionality.
With this setup, employees can query across ticketing systems, messaging platforms, and shared drives, all through a simple chat-like interface. The system responds with contextual answers, saving time that was once lost to manual digging or asking around.
Quality Control & Visual Inspection
While predictive maintenance keeps machines running, generative AI in quality control ensures they produce flawless outputs. Instead of relying solely on manual checks or pre-labeled datasets, GenAI enables faster, more accurate defect detection and can even generate synthetic images to train inspection models before real-world failures occur.
Real-Time Defect Detection Using GenAI
Modern manufacturing lines now deploy computer vision systems powered by GenAI that can:
- Analyze product images frame-by-frame, detecting surface anomalies, missing parts, or misalignments in milliseconds
- Catch subtle issues like tiny surface variations that humans or rule-based systems might miss.
- Improve automatically as they process more images, without needing full retraining
⚠️ Note: GenAI works best when combined with existing computer vision tools and high-quality image data. It doesn’t replace traditional inspection but adds an extra layer of intelligence and adaptability.
Synthetic Image Generation for Training Models
Sometimes factories don’t have enough real images of defects especially the rare ones. That’s where generative AI helps by creating synthetic defect images that look like real faults.
This allows inspection systems to learn and detect problems early, even if they haven’t happened on the line yet.
Benefits of using synthetic data:
- Speeds up training of visual inspection models without needing to wait for real failures
- Adds more variety to your defect examples, improving detection
- Helps launch new inspection tools earlier especially for new products
⚠️ Note: Synthetic data works best when combined with real images. It doesn’t fully replace actual failure samples but helps fill in gaps when real-world data is limited or hard to collect.
Example: Bosch’s Synthetic Data for AI-Based Image Inspection
Bosch ran into a common problem: their production was so efficient that there weren’t enough examples of defects to train their vision systems.
Their solution? Use generative AI to create over 15,000 artificial defect images, each based on a few real-world samples. These synthetic visuals were so detailed that Bosch’s AI models could learn how to detect rare, nuanced flaws with remarkable precision long before they appeared on actual products.
That meant less time training systems, faster deployments, and more consistent product quality across facilities.
Supply Chain Optimization
A smooth-running supply chain is what keeps production moving but unpredictability is the new normal. Whether it’s a sudden spike in demand or a shipment delay across the globe, manufacturers are under pressure to act fast.
Generative AI helps by adding foresight to operations. Instead of simply managing problems after they occur, it helps supply chain teams predict, simulate, and prepare so they can respond with confidence, not guesswork.
Demand Forecasting, Risk Simulations, Smart Routing
What GenAI Can Help You Do:
- Forecast demand more accurately: Uses past sales, seasonal trends, and even market changes to predict what you’ll need so you don’t overstock or run short.
- Plan for disruptions before they hit: GenAI can simulate “what-if” events like supplier delays or bad weather and suggest ways to reduce the impact.
- Suggest better delivery routes: Takes into account things like fuel use, traffic, and delivery time helping improve both cost and sustainability.
⚠️ Note: These insights depend on quality data from supply chain systems. GenAI makes predictions and suggestions but still needs integration with ERP, logistics, and external data sources to deliver real value.
GenAI for Inventory Efficiency and Resilience
Managing inventory is a constant balancing act. Too much stock ties up money. Too little causes delays and missed sales. Generative AI helps manufacturers find the right middle ground without relying on guesswork.
Here’s how it works:
- Predicts stock needs by learning from past sales, seasonal trends, supplier delivery times, and product demand
- Spots issues early like sudden drops in supply or spikes in customer orders.
- Suggests quick fixes such as shifting stock from one location to another to avoid bottlenecks or shortages.
⚠️ Note: GenAI doesn’t make these decisions alone. It supports your planners and works best when integrated with existing supply chain or ERP systems.
Example: Microsoft Dynamics 365 Copilot
Microsoft’s integration of GenAI into its Supply Chain Center via Dynamics 365 Copilot is a compelling real-world case.
This AI assistant doesn’t just crunch numbers it correlates supply chain disruptions (like extreme weather, geopolitical risks, or raw material shortages) with real-time order impact. Then, it offers proactive guidance, even drafting communication to affected vendors or logistics partners.
Ready to Bring GenAI to Your Factory Floor?
Supercharge your manufacturing operations with AI-powered solutions designed for real-time decision-making, intelligent automation, and scalable innovation.
Building Smarter Factory Systems with Generative AI
Early GenAI in manufacturing focused on task automation. Now, it’s enabling system-level autonomy. Smart factories are evolving into self-learning environments where generative AI powers real-time decisions, dynamic control logic, and predictive simulations.
At the core of this transformation are three enablers:

Digital Twins, PLC Code Generation & Adaptive Machinery
One of the most exciting integrations is happening at the machine level, where generative AI collaborates with digital twin models to simulate, refine, and even auto-generate control logic.
- Digital twins now replicate real-time production states, from mechanical stress levels to energy usage, enabling deeper insight into operational bottlenecks.
- GenAI can translate operator prompts into PLC code, generating and testing logic blocks for programmable machines slashing engineering time and reducing human error.
- These models allow manufacturers to simulate configurations, stress-test parameters, and optimize machinery settings before implementing any changes on the shop floor.
Rather than relying on weeks of manual testing, engineers can iterate faster in silico first, in metal second.
Self-Optimizing Systems with GenAI Feedback Loops
Static processes are out. Self-regulating systems are in.
Generative AI can act as the orchestrator for adaptive machinery by establishing closed feedback loops between data sources (like sensors, quality scans, and ERP inputs) and system control logic.
Here’s how it works:
- It analyzes output quality, operational parameters, and external factors (like material variability or environmental conditions).
- It then adjusts machine behaviors like speed, pressure, sequence logic based on predictive patterns.
- Over time, GenAI models learn optimal configurations and create decision trees to recommend or implement changes automatically.
Real-Time Decision-Making in Connected Operations
At the systems level, GenAI is now acting as a real-time decision engine not just guiding human operators but augmenting or replacing reactive decision-making altogether.
From rerouting work orders to balancing energy usage across machines, its contributions go far beyond analytics:
- In connected factories, GenAI systems correlate live sensor data with MES (Manufacturing Execution System) inputs to fine-tune operations on the fly.
- It helps optimize multi-line coordination like if one process goes down, the AI identifies the next best path for throughput with minimal impact.
- In high-mix manufacturing, it replans schedules dynamically based on order priority, material availability, and capacity constraints.
Challenges and Risks of Adopting GenAI in Manufacturing
No technological leap comes without friction. While generative AI holds immense promise for manufacturing, it also opens up a series of practical and ethical challenges that can’t be ignored. These aren’t just abstract risks they’re real-world complexities that can determine the success or failure of GenAI integration on the factory floor.

Data Bias, Hallucination, Security and Privacy Concerns
GenAI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If that data contains mislabeled parts or gaps, the model may confidently recommend flawed components exposing manufacturers to critical risks. This is the danger of data bias.
Compounding the issue is AI hallucination, where models fill in gaps with fabricated but believable outputs. In high-stakes environments, such as quality control or safety, even minor hallucinations can lead to costly errors. Add to that the handling of sensitive operational data, and GenAI must be implemented with strong data governance, security, and ethical oversight.
Mitigation Tip: Implement strong data validation pipelines, restrict model access to confidential data, and leverage GenAI platforms with built-in compliance support.
Integration with Legacy Systems and Workforce Readiness
Many factories still rely on aging but essential infrastructure like proprietary PLCs, siloed MES systems, and fragmented ERP platforms. Without a strategic integration plan, introducing GenAI can lead to disconnected workflows and underwhelming ROI.
Success depends on building middleware and modular APIs that bridge GenAI with existing systems. Just as important is preparing the workforce. Line operators and floor managers don’t need to be AI experts but they do need intuitive tools, clear interfaces, and practical training to fully leverage GenAI’s value.
Solution: Focus on co-pilot style experiences, invest in change management, and upskill teams in using GenAI outputs as decision support not decision replacements.
Need for Human Oversight and Explainability
A major hurdle in GenAI adoption is explainability. Unlike rule-based systems, GenAI often functions as a “black box,” delivering outcomes without clear reasoning. This lack of transparency can erode trust especially in regulated industries where traceability is non-negotiable.
To address this, manufacturers must adopt explainable AI (XAI) frameworks that show confidence levels, decision logic, and rationale behind every GenAI output. With global regulators increasingly demanding auditability, explainability isn’t just about compliance it’s critical for safe and reliable operations.
Best Practice: Build workflows where humans validate GenAI suggestions, and always retain the ability to override or escalate decisions.
Roadmap to Implementing GenAI in Manufacturing
For most manufacturers, the excitement around generative AI is real but so is the uncertainty. It’s no longer a question of if GenAI will impact the factory floor, but how to deploy it in ways that actually move the needle.
Implementing generative AI in manufacturing isn’t just about adding new tech it’s about rethinking how people, machines, and data collaborate. A structured, purpose-driven roadmap can help manufacturers move beyond pilots and start delivering real-world impact with GenAI.
Step 1: Evaluate Existing Workflows and Pain Points
Before introducing GenAI, manufacturers need to map out current processes from product development and maintenance to quality assurance and supply chain operations. This helps identify:
- High-friction manual tasks
- Repetitive decision-making flows
- Data-rich environments ideal for GenAI application
Start with a maturity assessment first identify not just inefficiencies, but where GenAI could augment human decision-making or automate knowledge-intensive tasks.
Step 2: Define Target Use Cases and KPIs
It’s tempting to jump in with generalized tools like ChatGPT. But real value lies in domain-specific GenAI applications tailored to your factory’s context.
Prioritize use cases that:
- Solve high-impact problems (e.g., unplanned downtime, slow quote generation)
- Have clean or easily collectible data
- Align with broader digital transformation goals
Example KPIs: reduced design-to-production time, fewer maintenance-related downtimes, improved quote accuracy, or lower defect rates.
Step 3: Choose the Right GenAI Model Architecture
The next critical decision is model sourcing and deployment strategy:
| Option | Pros | Considerations |
| Vendor-Hosted GenAI (e.g., Azure OpenAI) | Low upfront cost, quick start | Less customization, external data exposure |
| Open-Source Models (e.g., LLaMA, Mistral) | High flexibility, data control | Requires in-house expertise |
| Custom-Built Models | Tailored to your data & domain | High resource investment |
Consider model explainability, latency, integration needs, and cost per inference as part of your decision criteria.
Step 4: Build the Right Infrastructure
Running GenAI at scale requires infrastructure that’s secure, scalable, and performance-optimized.
Key infrastructure layers:
- Data Pipeline: Clean, well-labeled data from PLCs, IoT, ERP, MES
- Compute Resources: GPUs (cloud or on-prem) to handle large model workloads
- APIs & Interfaces: User-friendly, role-specific, integrated into existing workflows
Consider edge deployment if latency, bandwidth, or data security are top concerns especially in real-time use cases like visual inspection.
Step 5: Pilot, Measure, Iterate
GenAI adoption isn’t a one-and-done initiative. Start small.
- Run limited-scope pilots tied to measurable KPIs
- Collect operator feedback
- Refine prompts, outputs, and workflows
- Expand only after confirming ROI or operational gains
The most successful manufacturers treat GenAI as an iterative process for continuous learning, improving, and adapting to real-world feedback.
The Future of Generative AI in Manufacturing
The evolution of generative AI in manufacturing is moving far beyond initial pilot applications. What began with design generation and predictive maintenance is now branching into immersive, highly integrated ecosystems like merging AI with advanced robotics, IIoT, AR/VR, and self-adaptive systems. As manufacturers shift from augmentation to autonomy, the boundaries of what’s possible are expanding in real time.]
AR/VR, Robotics, and IIoT
The convergence of generative AI, industrial IoT, and immersive technologies is creating a new paradigm for smart factories. GenAI is becoming the cognitive engine behind:
- AI-enhanced robotics: Robots that interpret instructions from natural language prompts and respond in context.
- AR/VR-based operations: Real-time assistance through wearable devices, powered by AI-generated work instructions, maintenance walkthroughs, and safety alerts.
- Connected IIoT systems: Sensor-rich environments feeding data into GenAI models to optimize energy usage, resource allocation, and machine configurations.
These integrations allow manufacturers to simulate operations, test alternate production scenarios, and rapidly iterate without impacting live systems.
Imagine an operator receiving step-by-step visual instructions on smart glasses while AI reconfigures the production layout in a simulated twin all within the same workflow.
Redefining the Workforce
As GenAI takes on more complex, cognitive tasks, the human workforce is evolving alongside it:
Key roles now entering the manufacturing space:
- Prompt Engineers: Experts who craft precise, contextual prompts to drive GenAI output accuracy and reliability.
- Digital Twin Architects: Professionals designing synchronized virtual replicas of assets, products, and workflows powered by generative models.
- AI Trainers & Orchestrators: Specialists responsible for model fine-tuning, human feedback loops, and managing GenAI performance in real-world scenarios.
From Augmentation to Autonomy
The next frontier moves beyond basic automation, aiming for factories that can self-correct, self-optimize, and continuously learn on their own. In the near future, we can expect:
- Closed-loop feedback systems where GenAI adjusts production schedules and machine settings based on real-time data.
- Zero-downtime predictive models that preemptively reallocate resources or suggest corrective actions before issues arise.
- Adaptive supply chains that reshape themselves based on demand signals, inventory changes, and global logistics conditions guided by AI simulations.
Conclusion
Generative AI is reshaping the manufacturing landscape enhancing how products are designed, machines are maintained, teams are trained, and supply chains are managed. As a foundational layer of smart manufacturing, it enables faster decisions, greater precision, and improved efficiency across operations.
Manufacturers who approach GenAI in manufacturing with a clear strategy, focused use cases, and cross-functional collaboration are better positioned to see measurable outcomes. It’s not just about adopting new tools by aligning technology with business goals.